The Unseen Backbone of Modern Electronics
In our digitally-driven world, we are surrounded by an ever-growing constellation of electronic devices, from the smartphones in our pockets to the complex systems guiding vehicles. At the heart of nearly every one of these technological marvels lies a humble yet essential component: the Printed Circuit Board, or PCB. This foundational element is the central nervous system of electronics, providing both the physical structure and the electrical pathways that allow components to communicate and function. The journey from a simple idea to a fully functional device begins with a meticulous process of PCB design, a discipline that blends artistry with engineering precision to create the blueprints for our digital age.

From Concept to Blueprint: The Intricacies of PCB Design
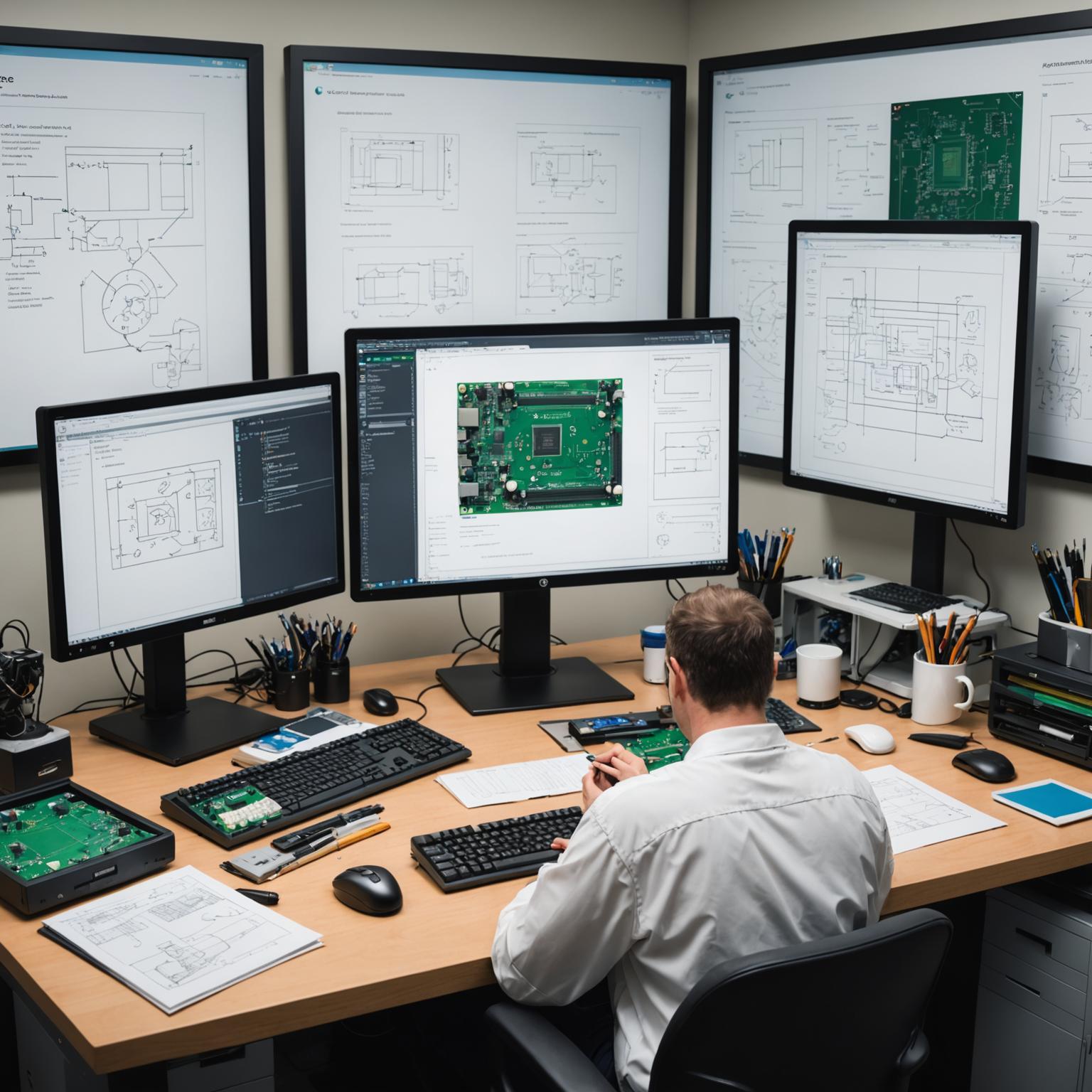
Creating a PCB is far more than just connecting dots on a board. The process of PCB design is an intricate dance of planning and precision. It starts with a schematic, a conceptual diagram that maps out every component and its connections. This blueprint is then translated into a physical layout, where engineers must strategically place components to optimize performance, manage heat, and minimize electrical noise. They carefully route copper traces—the thin lines that act as wires—to create a complex web of connectivity. A well-executed design ensures not only that the device works as intended but also that it is reliable, durable, and can be manufactured efficiently. It’s a stage where foresight and expertise prevent future failures and pave the way for a successful product.
The Crucial First Step: The Role of PCB Prototyping
Before a design can be mass-produced, it must be tested and validated. This is the critical role of PCB prototyping. A prototype is the first physical embodiment of the digital design, a tangible test article that allows engineers to see their creation in the real world. This phase is indispensable for debugging and refinement. Engineers can test the board’s electrical characteristics, ensure all components fit and function correctly, and evaluate its overall performance under various conditions. PCB prototyping acts as a crucial bridge between the theoretical design and the final, manufacturable product, saving significant time and resources by catching potential flaws early in the development cycle. It is the moment of truth where a concept proves its viability.
The Symphony of Creation: Understanding PCB Assembly Services
Once a prototype has been perfected, the design moves into production. This is where PCB assembly services come into play, transforming bare boards into fully functional electronic assemblies. This process is a marvel of automation and precision. Using advanced machinery, components are rapidly and accurately placed onto the board. Techniques like Surface Mount Technology (SMT) involve soldering minuscule components directly onto the board’s surface, while Through-Hole Technology (THT) is used for larger, more robust components. These expert PCB assembly services orchestrate a complex symphony of robotics and skilled technicians to populate thousands of boards with flawless consistency, ensuring that every single unit meets the exact design specifications.
Bending the Rules: The Rise of the Flexible PCB
Innovation in electronics is not just about making things smaller and faster; it’s also about making them fit into new and unconventional forms. This is where the Flexible PCB has revolutionized product design. Unlike their rigid counterparts, a Flexible PCB is built on a pliable base material, such as polyimide, allowing it to bend, twist, and fold to fit into tight or irregularly shaped spaces. This capability has unlocked new possibilities in wearables, medical implants, automotive dashboards, and aerospace applications where weight and space are at a premium. The Flexible PCB is a testament to the adaptability of circuit technology, enabling designers to break free from the constraints of flat, rigid boxes and integrate electronics seamlessly into almost any form imaginable.