The Critical Role of Precision in Medical Diagnostics
Medical diagnostics have evolved significantly, providing healthcare professionals with the tools and techniques necessary for accurate disease detection and treatment planning. Among the various diagnostic procedures, biopsies play an indispensable role in obtaining tissue samples for pathological examination. The success of these procedures, and consequently the accuracy of diagnoses, heavily relies on the quality and precision of the instruments used, such as Biopsy forceps. These specialized tools are engineered to retrieve tissue samples with minimal trauma to the patient while ensuring the integrity of the sample for analysis. As medical science advances, the demand for even more sophisticated and reliable instruments continues to grow, pushing innovation in their design and functionality.

Understanding Biopsy Procedures: A Cornerstone of Diagnosis
A biopsy is a medical procedure that involves taking a small sample of tissue from the body so it can be examined under a microscope. This examination helps doctors diagnose a variety of conditions, most notably cancer, but also inflammatory diseases, infections, and other cellular abnormalities. There are several types of biopsies, each suited to different parts of the body and varying conditions. Needle biopsies, for instance, use a special needle to extract tissue from organs or lumps beneath the skin. Endoscopic biopsies are performed during an endoscopy, where a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera is inserted into the body, allowing doctors to view internal organs and take tissue samples using tools passed through the endoscope. Surgical biopsies are performed if the area in question is difficult to reach or if a larger sample is needed. Regardless of the method, the primary goal remains the same: to obtain a representative tissue sample for accurate pathological assessment, which forms the basis of many critical treatment decisions.
Essential Biopsy Instruments for Modern Medicine
The accurate and safe retrieval of tissue samples during a biopsy hinges on the use of highly specialized biopsy instruments. These tools are designed with precision, patient safety, and sample integrity in mind. The range of instruments is diverse, catering to the specific requirements of different types of biopsies and anatomical locations. Common instruments include various types of needles for aspiration or core biopsies, dermatomes for skin biopsies, and specialized forceps and snares for endoscopic procedures. Each instrument is meticulously crafted from medical-grade materials to ensure biocompatibility, sterility, and durability. The design often incorporates features that enhance maneuverability, control, and the ability to obtain an adequate, high-quality sample without causing unnecessary damage to surrounding tissues. The collective aim of these biopsy instruments is to empower medical professionals to perform procedures efficiently and effectively, leading to better patient outcomes.
A Closer Look at Biopsy Forceps: Design and Functionality
Biopsy forceps are among the most commonly used tools for tissue sampling, especially during endoscopic procedures like colonoscopies or gastroscopies. These instruments are characterized by a pair of cupped jaws at the distal end, which are used to grasp and excise small pieces of tissue. The design of these forceps can vary significantly based on their intended use. For example, some forceps have smooth cups for delicate tissues, while others may have serrated edges or a central spike for a better grip on tougher or more slippery tissues. The choice of forceps depends on the type of tissue being sampled, its location, and the specific requirements of the procedure. High-quality Biopsy forceps ensure a clean cut, minimizing tissue trauma and preserving the architecture of the sample, which is crucial for accurate histological interpretation. The shaft of the forceps is typically flexible for navigation through endoscopes but rigid enough to transmit the necessary force to the jaws. Modern forceps also focus on ergonomic handles to provide the operator with precise control and comfort during the procedure.
Innovations in Medical Biopsy Tools: Enhancing Precision and Safety
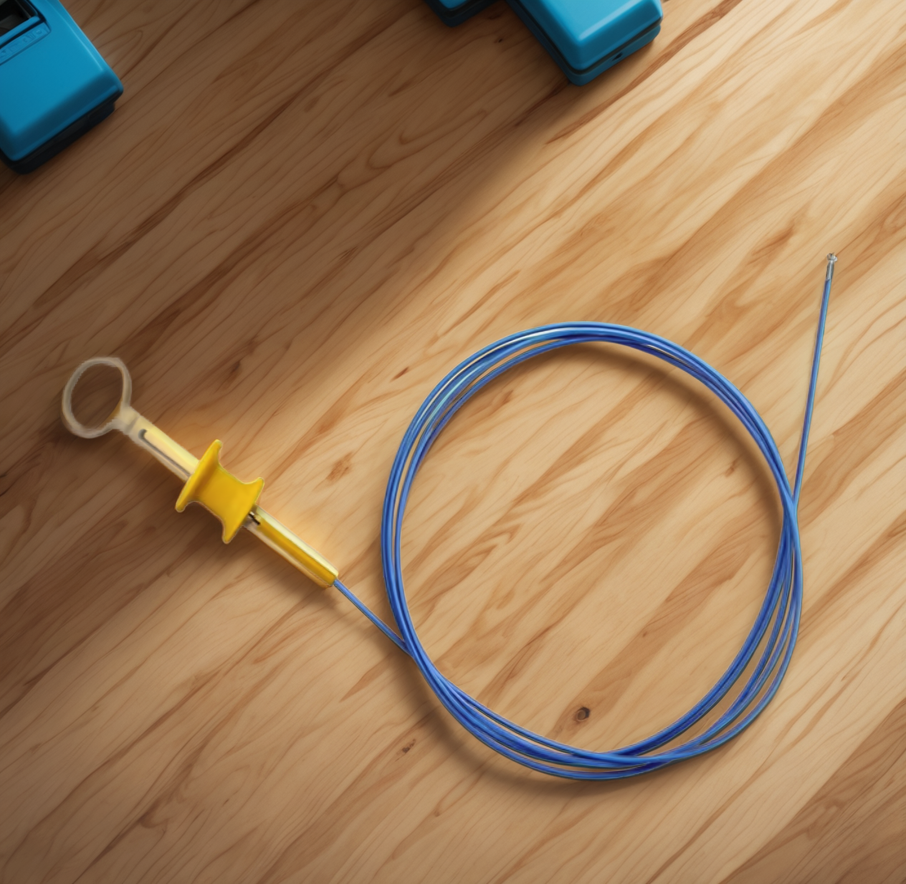
The field of medical biopsy tools is continually evolving, driven by the need for greater precision, improved patient safety, and enhanced procedural efficiency. Innovations span material science, mechanical design, and ergonomic considerations. For example, newer instruments often utilize advanced alloys that offer a superior combination of strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. The tips of these tools, whether they are forceps’ jaws or snare loops, are engineered with micro-precision to ensure clean tissue acquisition and minimize crush artifacts. Consider, for instance, advanced endoscopic snare systems; while not strictly forceps, these medical biopsy tools exemplify modern engineering with features like high-quality, medical-grade cables offering superior durability and flexibility, ensuring seamless maneuverability. The ergonomic design of handles is another critical area of innovation. Intuitive control mechanisms, comfortable grips, and lightweight construction help reduce operator fatigue, especially during lengthy procedures, allowing for sustained precision. These advancements translate directly into better sample quality, reduced procedure times, and improved patient comfort, significantly impacting diagnostic accuracy and overall care.
The Endoscopic Snare System: A Paradigm of Modern Instrument Design
While Biopsy forceps are a staple, other sophisticated medical biopsy tools like endoscopic snare systems highlight the technological progress in tissue acquisition. Such systems are often designed for procedures like polyp removal, where a loop of wire is used to encircle and excise tissue. The design principles behind these advanced tools mirror the desired qualities in all high-end biopsy instruments. For example, an Endoscopic Snare System might feature a sleek, modern design with a vibrant, high-visibility cable made from medical-grade material for superior durability and flexibility. The sheath might be streamlined for optimal handling, enabling intuitive movement in tight spaces. The core of such a product is often its precisely engineered snare loop—thin, yet incredibly strong, calibrated for clean cuts while maintaining utmost control. The handle mechanisms in these advanced tools often feature intuitive sliders or rings for effortless operation, crafted from materials that ensure robust longevity and minimize weight. These features, whether found in snares or the latest generation of biopsy forceps, underscore a commitment to enhancing the practitioner’s ability to perform complex procedures with greater confidence and success, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes through more accurate and efficient tissue removal for diagnostic purposes.
Choosing and Maintaining Biopsy Instruments for Optimal Performance
Selecting the appropriate biopsy instruments is crucial for the success of any biopsy procedure. Factors to consider include the type of biopsy being performed, the anatomical location, the characteristics of the target tissue, and the specific features of the instrument itself. For example, when choosing Biopsy forceps, considerations include the cup size and shape, the presence of a spike for better tissue anchoring, and the length and flexibility of the shaft. The material composition is also vital, ensuring biocompatibility and durability. Equally important as selection is the proper care and maintenance of these instruments. Most biopsy instruments, especially those used in endoscopic procedures, are designed for single-use to eliminate the risk of cross-contamination and ensure consistent performance. For reusable instruments, strict sterilization protocols must be followed. Proper handling, cleaning, and sterilization are essential to maintain the integrity of the instruments and, more importantly, to protect patient safety. Adherence to manufacturer guidelines for use and maintenance ensures that these critical tools perform optimally every time.
The Future Trajectory of Biopsy Technology
Looking ahead, the evolution of biopsy technology is poised to continue its rapid advancement. We can anticipate further integration of smart technologies, such as sensors providing real-time feedback or robotic assistance enhancing precision an_d control. Miniaturization will likely lead to even less invasive procedures, allowing access to previously difficult-to-reach areas with minimal patient discomfort. Material science will continue to play a pivotal role, with the development of new biocompatible materials offering enhanced properties like improved sharpness retention in cutting edges or better imaging compatibility. Furthermore, there’s a growing trend towards developing biopsy instruments that not only retrieve tissue but also offer immediate, on-site preliminary analysis capabilities. This could significantly speed up the diagnostic process. As our understanding of diseases at the molecular level deepens, the demand for biopsy instruments capable of obtaining high-quality, specific tissue samples, even at a cellular level, will drive further innovation, ensuring that these tools remain at the forefront of medical diagnostics and personalized medicine.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of High-Quality Biopsy Tools
In conclusion, biopsy procedures are a fundamental component of modern medical diagnostics, providing invaluable information for disease detection, staging, and treatment planning. The effectiveness of these procedures is inextricably linked to the quality, precision, and appropriateness of the biopsy instruments used. From sophisticated Biopsy forceps to advanced snare systems and innovative needle designs, each tool is engineered to meet specific clinical needs. Continuous innovation in the design, materials, and functionality of these medical biopsy tools ensures that healthcare professionals can perform biopsies with increasing accuracy, safety, and efficiency. As medical science progresses, the commitment to developing superior biopsy instruments will remain paramount, ultimately contributing to improved patient care and better health outcomes worldwide.